Coded Expression
"...we are in the end no more sophisticated than all sorts of simple programs, and all sorts of systems in nature."
- Stephen Wolfram on the Principle of Computational Equivalence
Coded Expression is a series of abstract visualizations in search of emergent patterns resulting from code. Borrowing concepts from calculus, algebra, noise analysis, cellular automata and other areas, standard and non-standard mathematical equations were tweaked, combined and applied to digital objects to generate interesting swarm behaviour, digital material properties, and shaders among other things.
View C# code here.
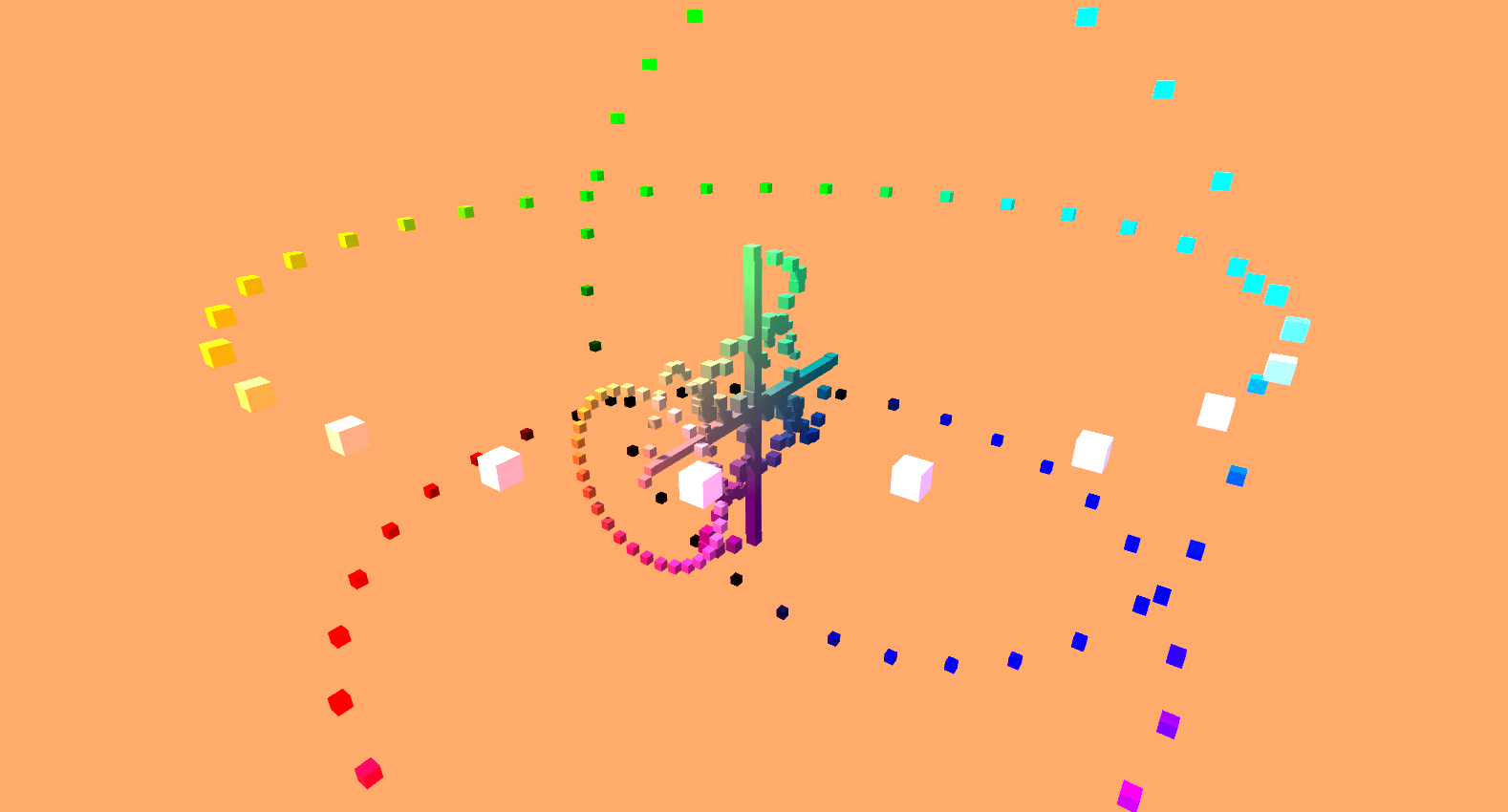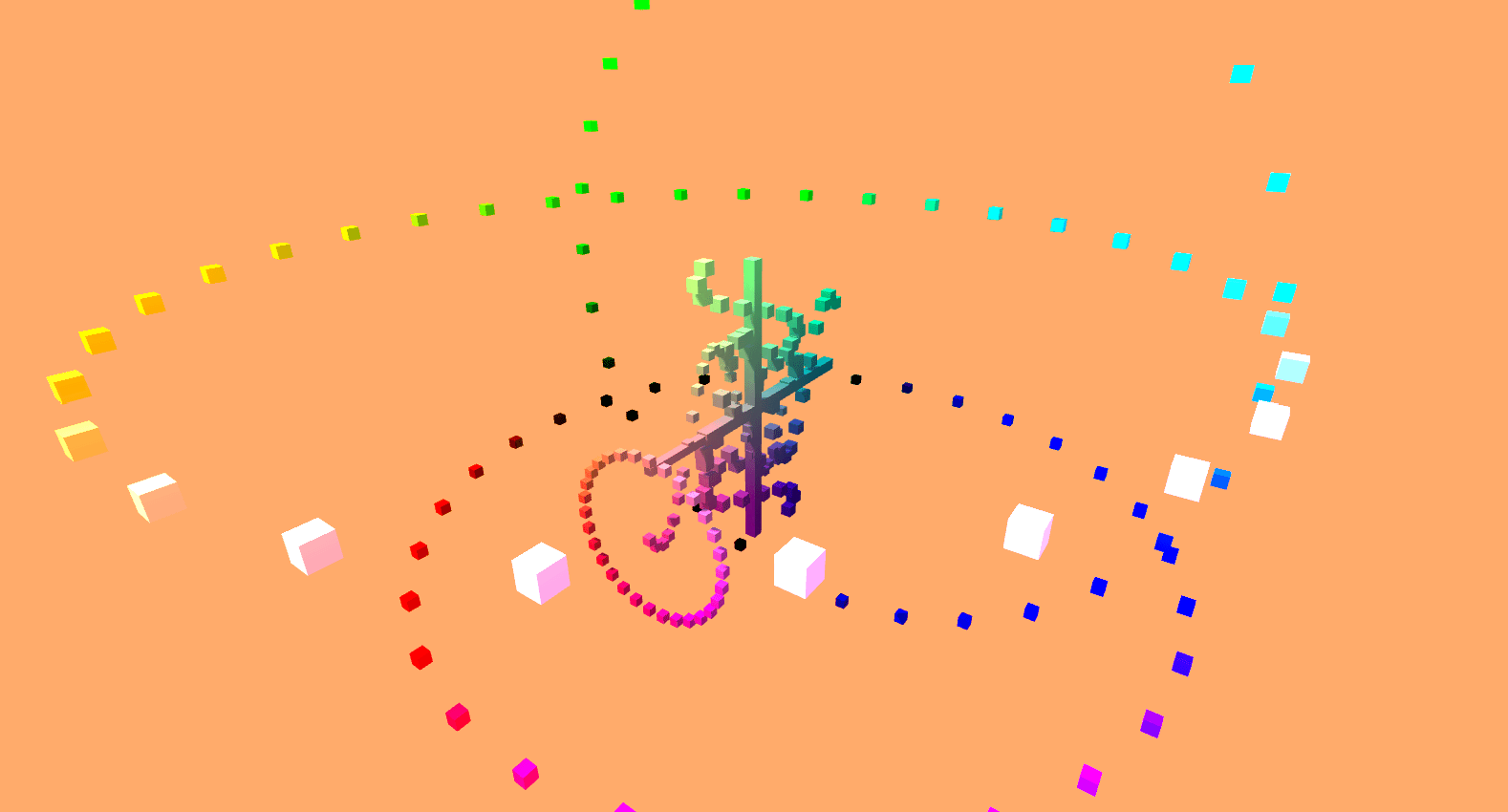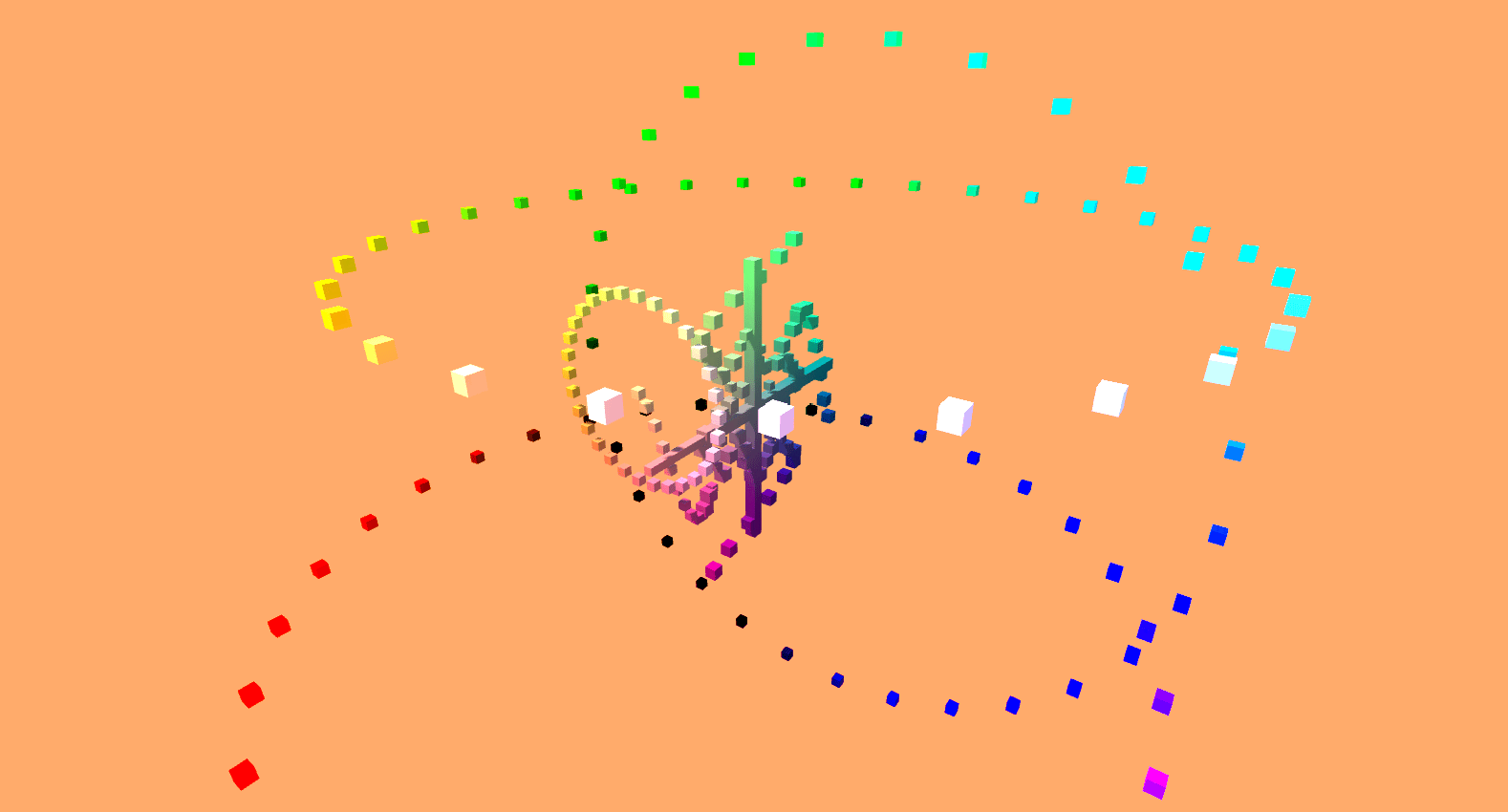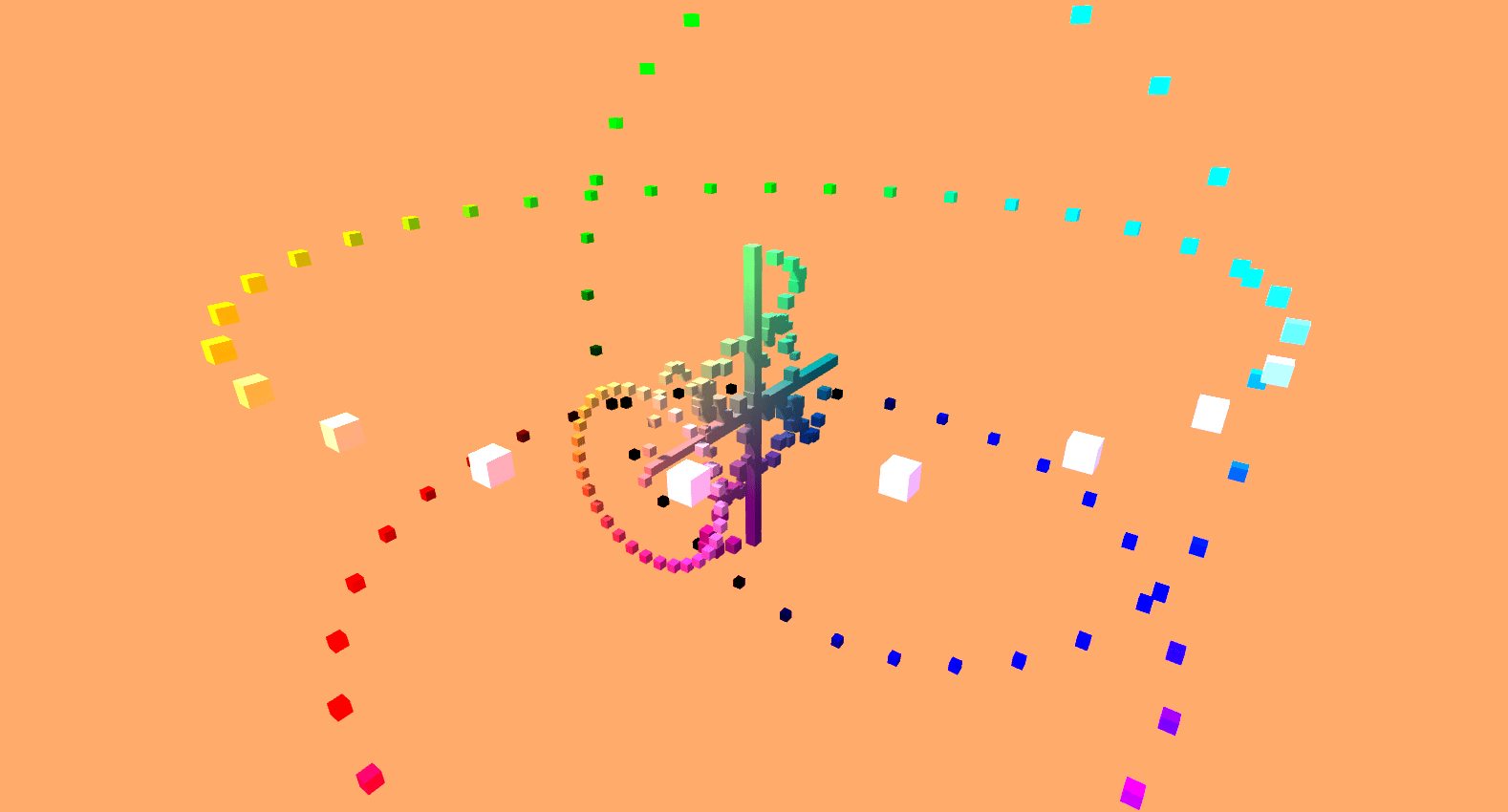
Sine it.
Using the inherently unique properties of a unit circle, and by applying basic trigonometry operations, a series of cubes were procedurally generated and animated to create what resembles an abstracted mail sorting system.



HSV disco
Here, a shader script was written to generate color data based on the parametric equation for an epicycloid with 3 and 4 cusps and applied to three spheres and a plane, respectively, to create a disco ball effect.
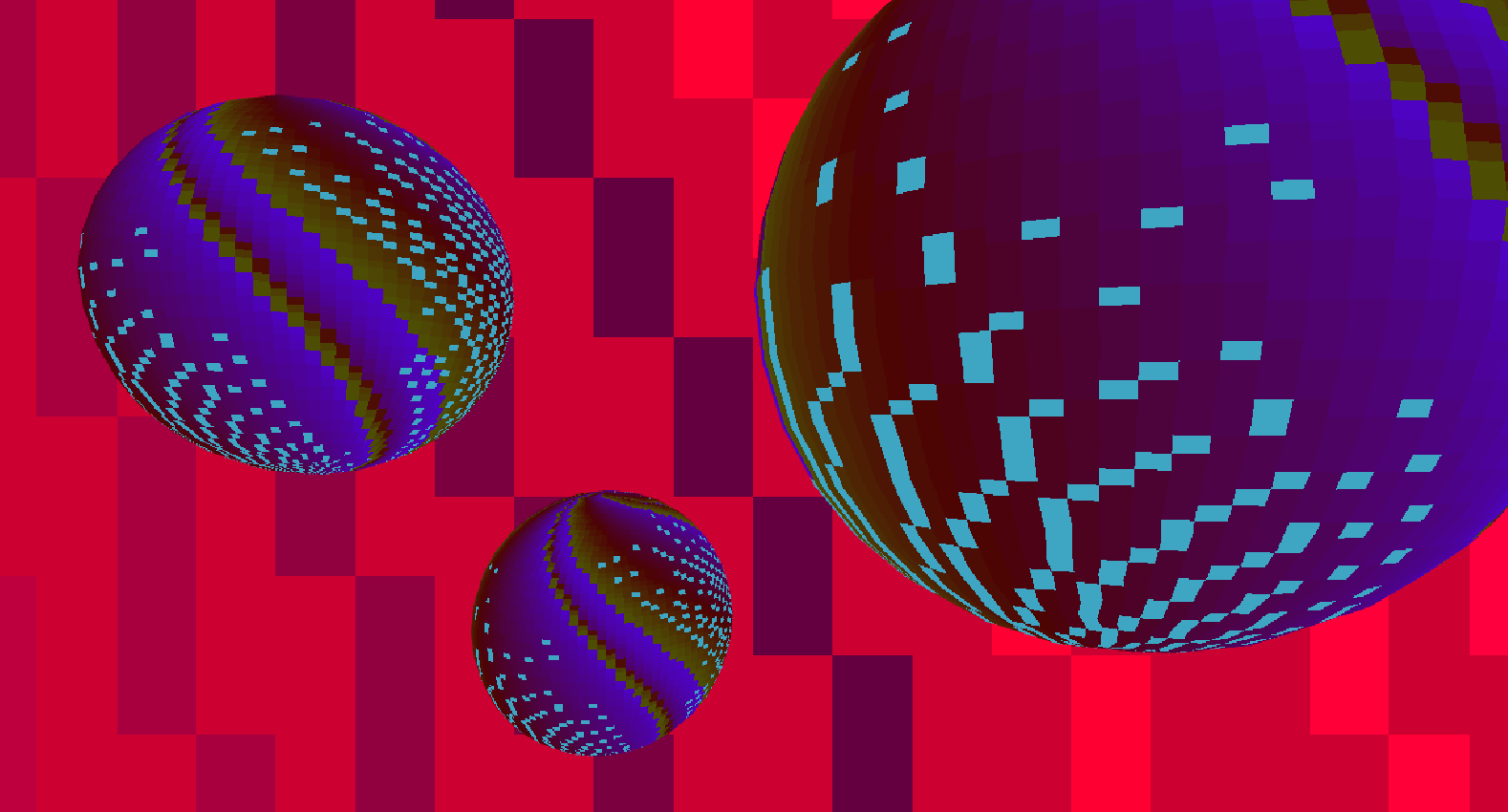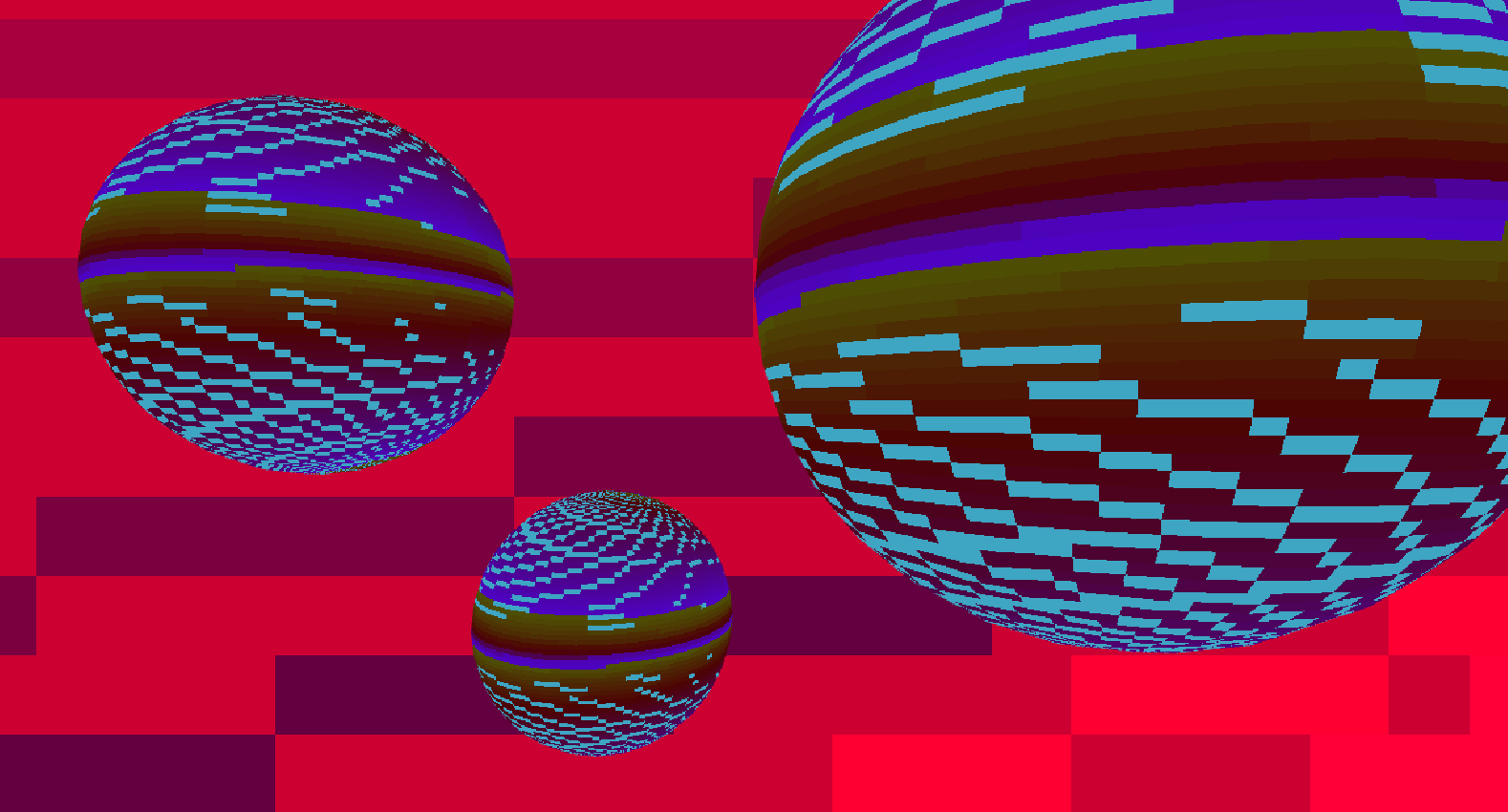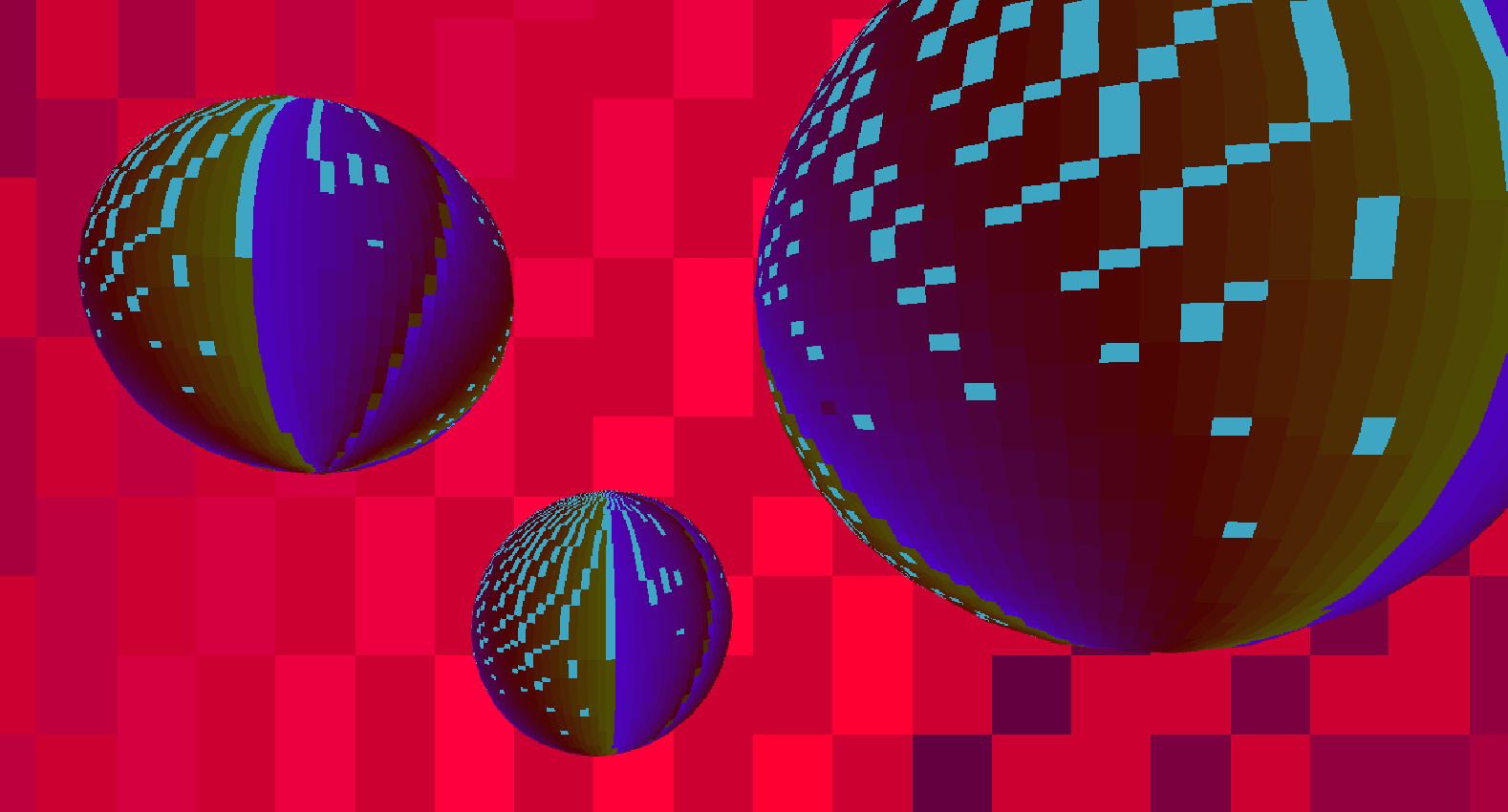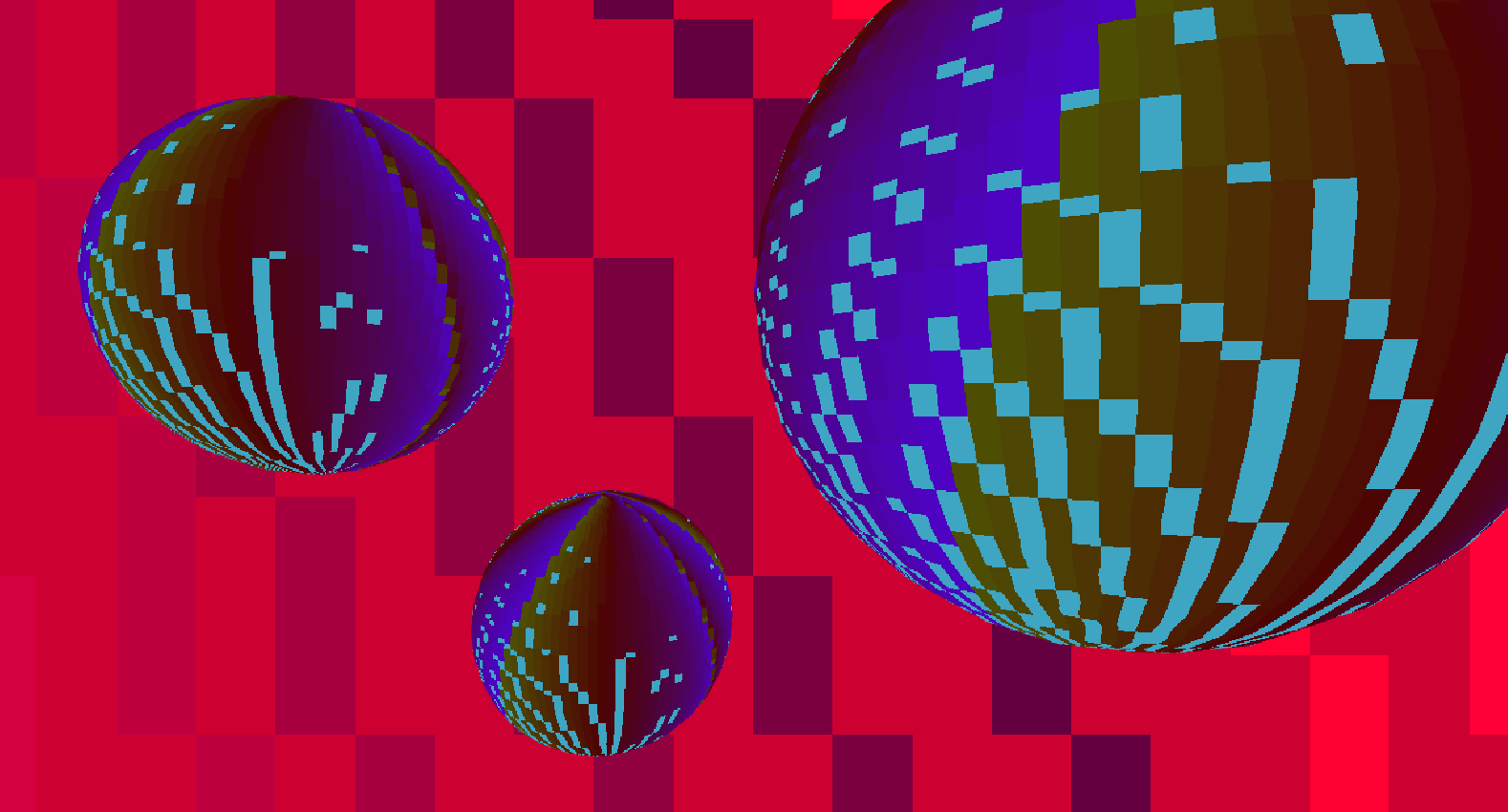
Ada, Ada
Ada K. Dietz is a well known American weaver whose book Algebraic Expressions in Handwoven Textiles still fascinates weavers and mathematicians to this day. Using her unique algebraic weaving scheme which employs the expansion of multivariate polynomials, a series of animated weaving patterns were generated.

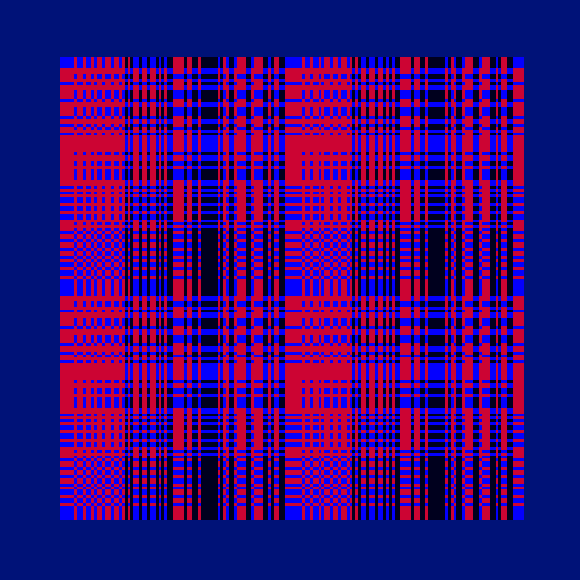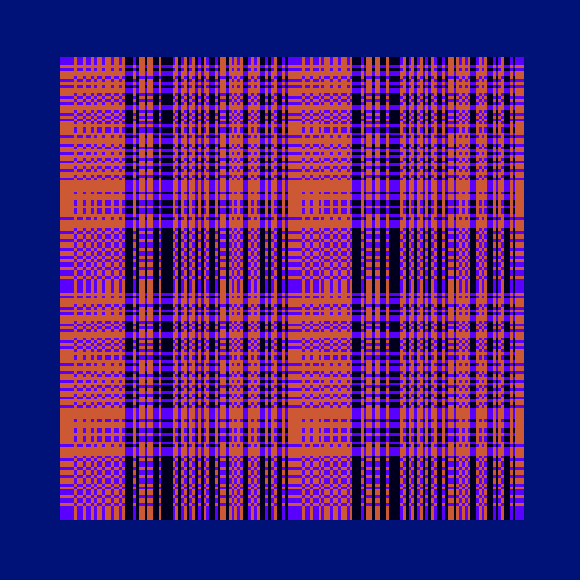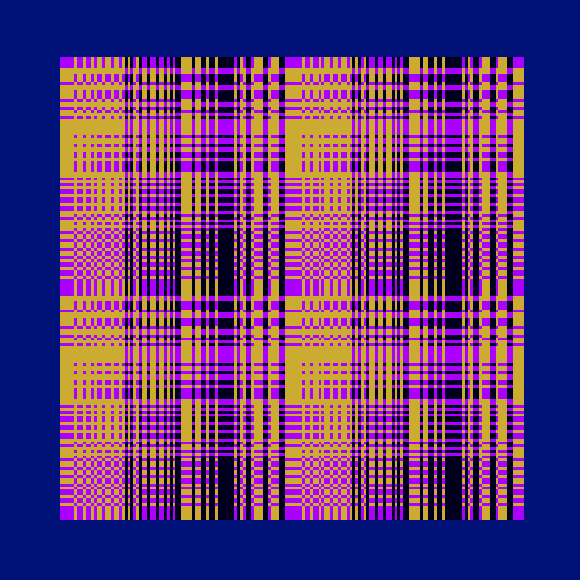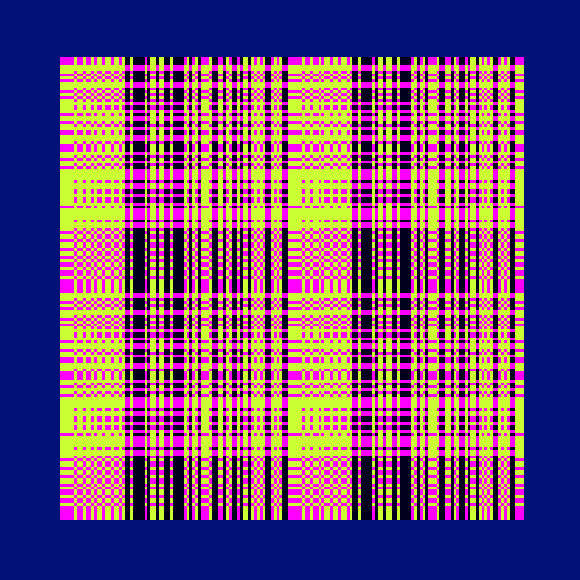
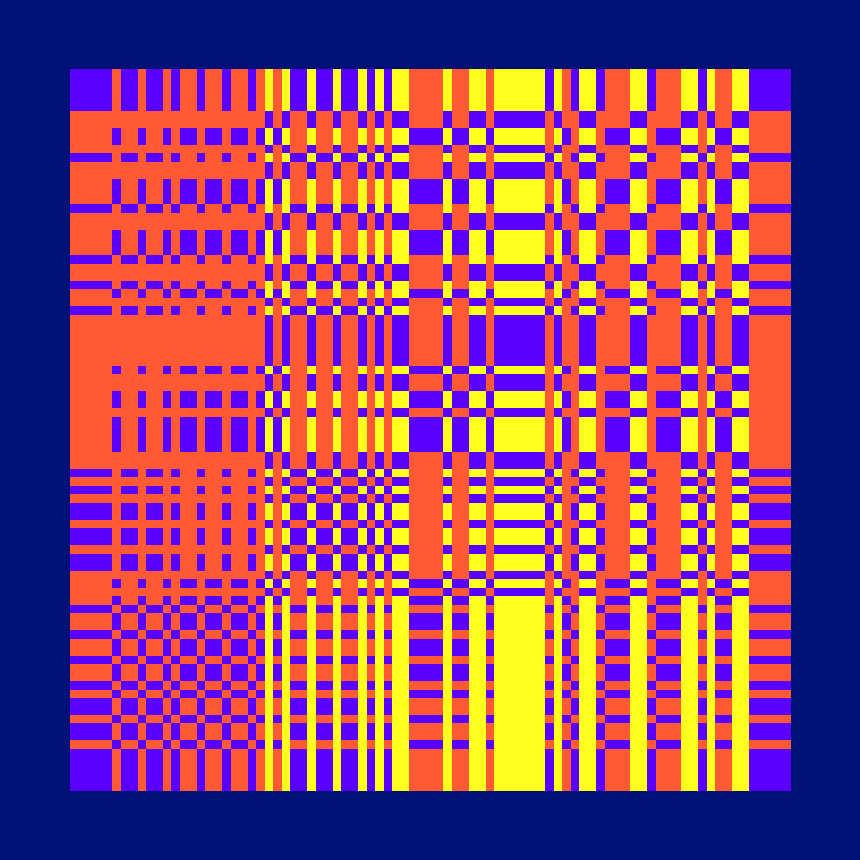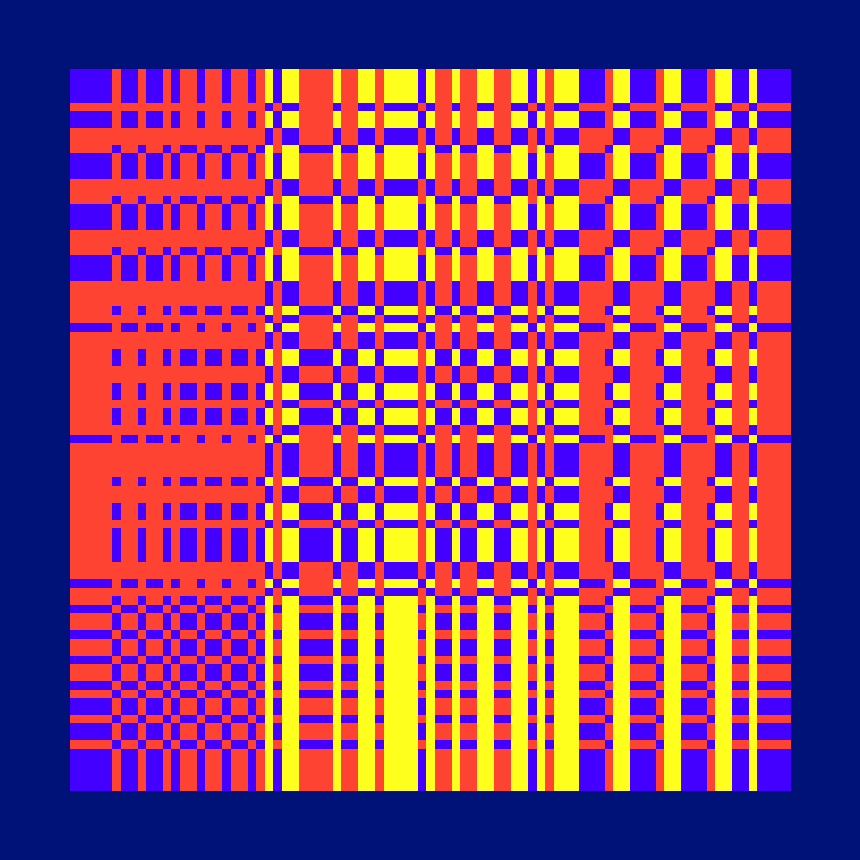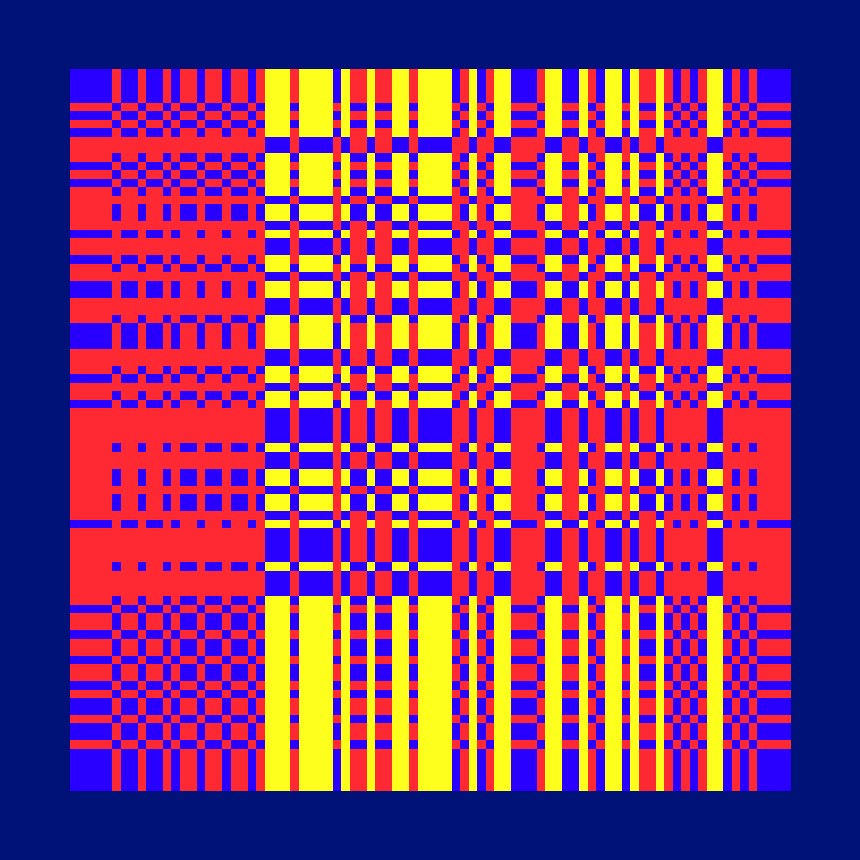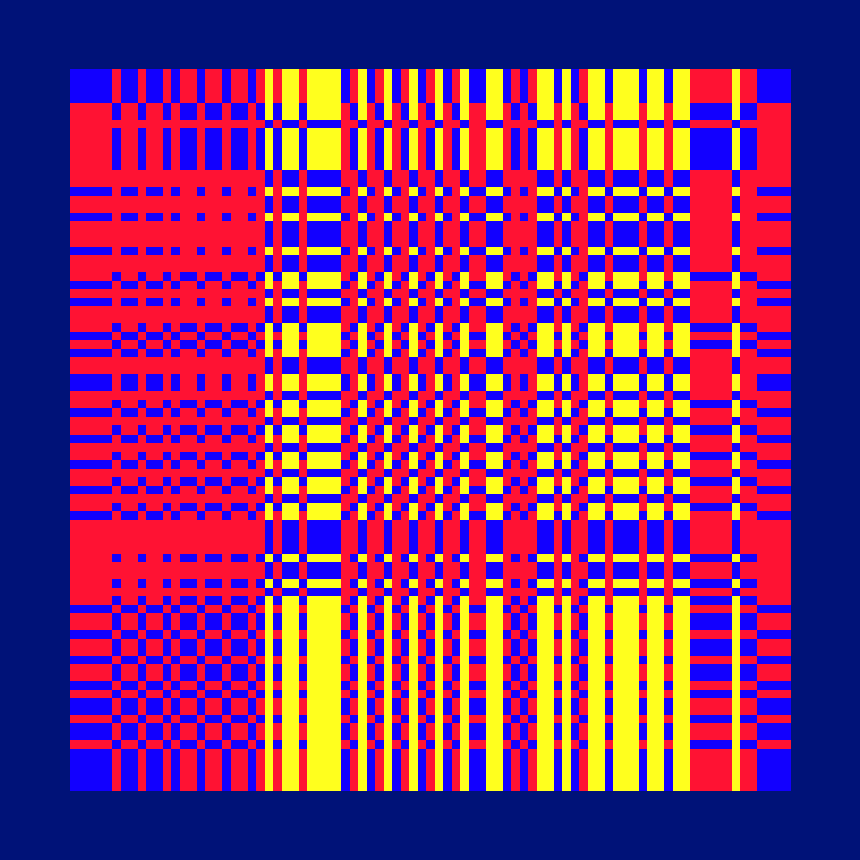
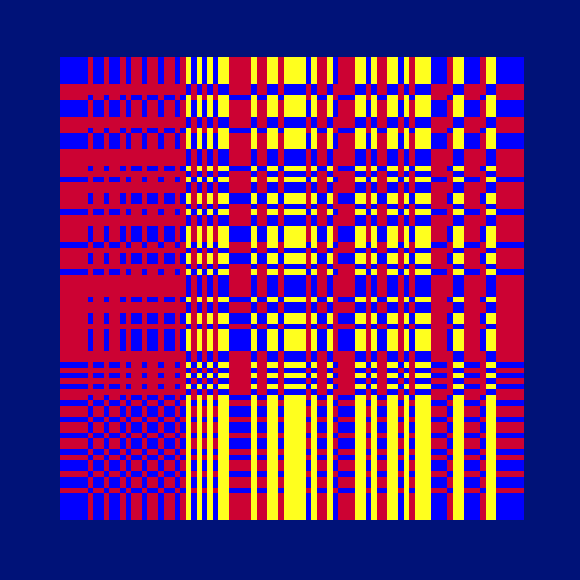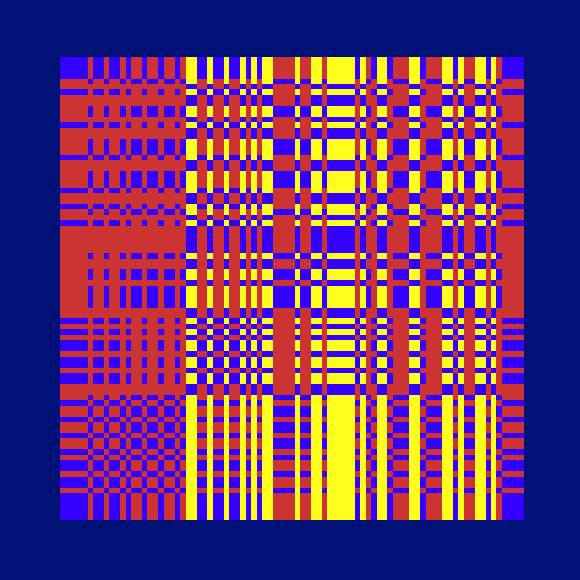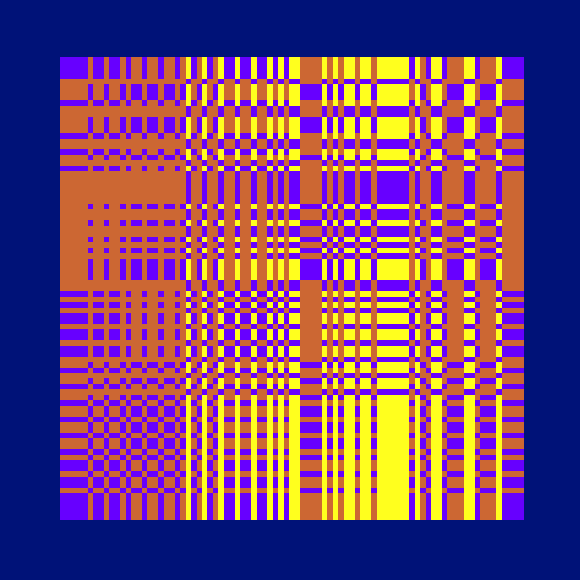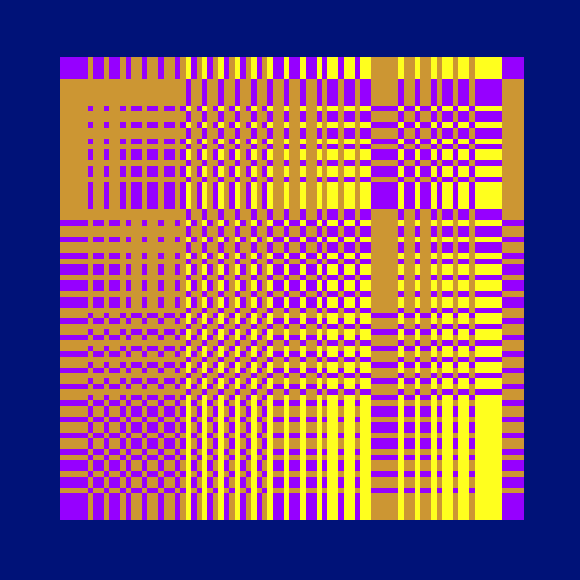

Trigonometric Hallucination
Originally conceptualized as a dragon's roar, an amorphous line animation was procedurally generated using another epicycloid equation. Random noise distorts the fluid line with user input.
Boids Revolt
Using Craig Reynolds' boid model, an amorphous material behaviour was simulated. The boid model is a distributed behavioural model - a form of distributed intelligence so to speak - simulating multi-agent systems such as flock of birds, herd of penguins and so on. The basic flocking model consists of three simple steering behaviors: separation, alignment and cohesion. The below simulation applies all three to a flock of 'boid' game objects which are then responding to the presence of an external agent - a target game object.

This Noisy Matter
This Noisy Matter is a material behaviour simulation using the Perlin noise flow field - a random sequence generator producing a more natural ordered, harmonic succession of numbers compared to the standard random() function and is often used for smoother textures and surfaces in motion picture visual FX.


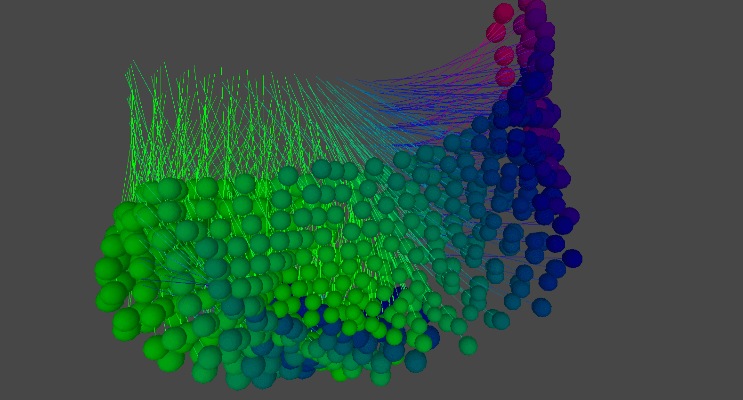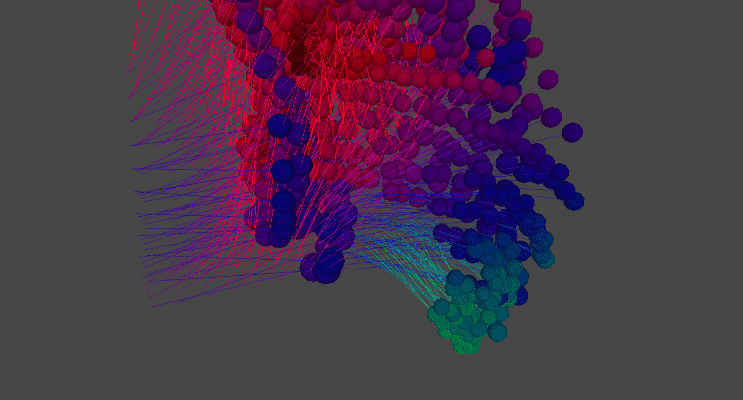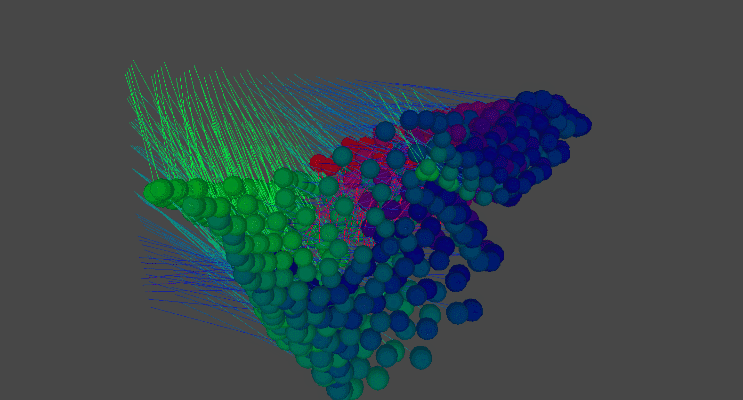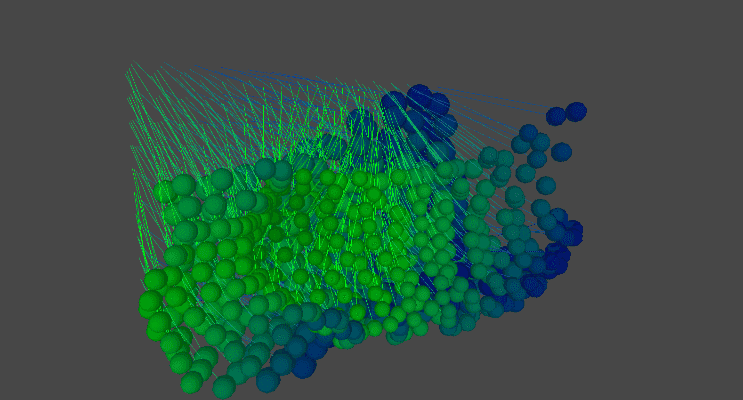

Medusa Tessellation
Medusa Tessellation is another simulation of material behaviour based on an 8x8 tiling of simulated threads. Each thread was procedurally generated to respond to physics and then animated through script to showcase the material's dynamic behaviour.
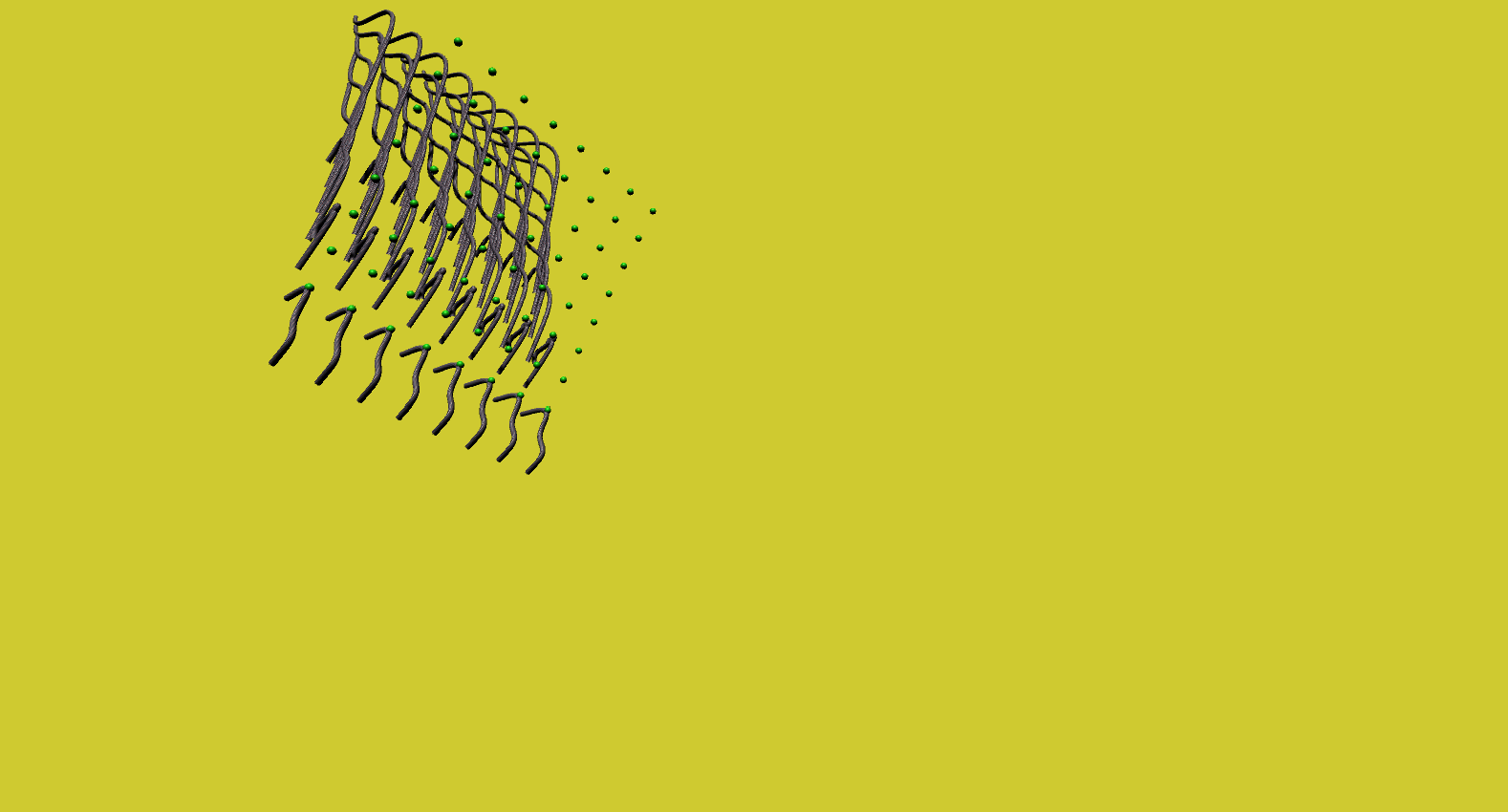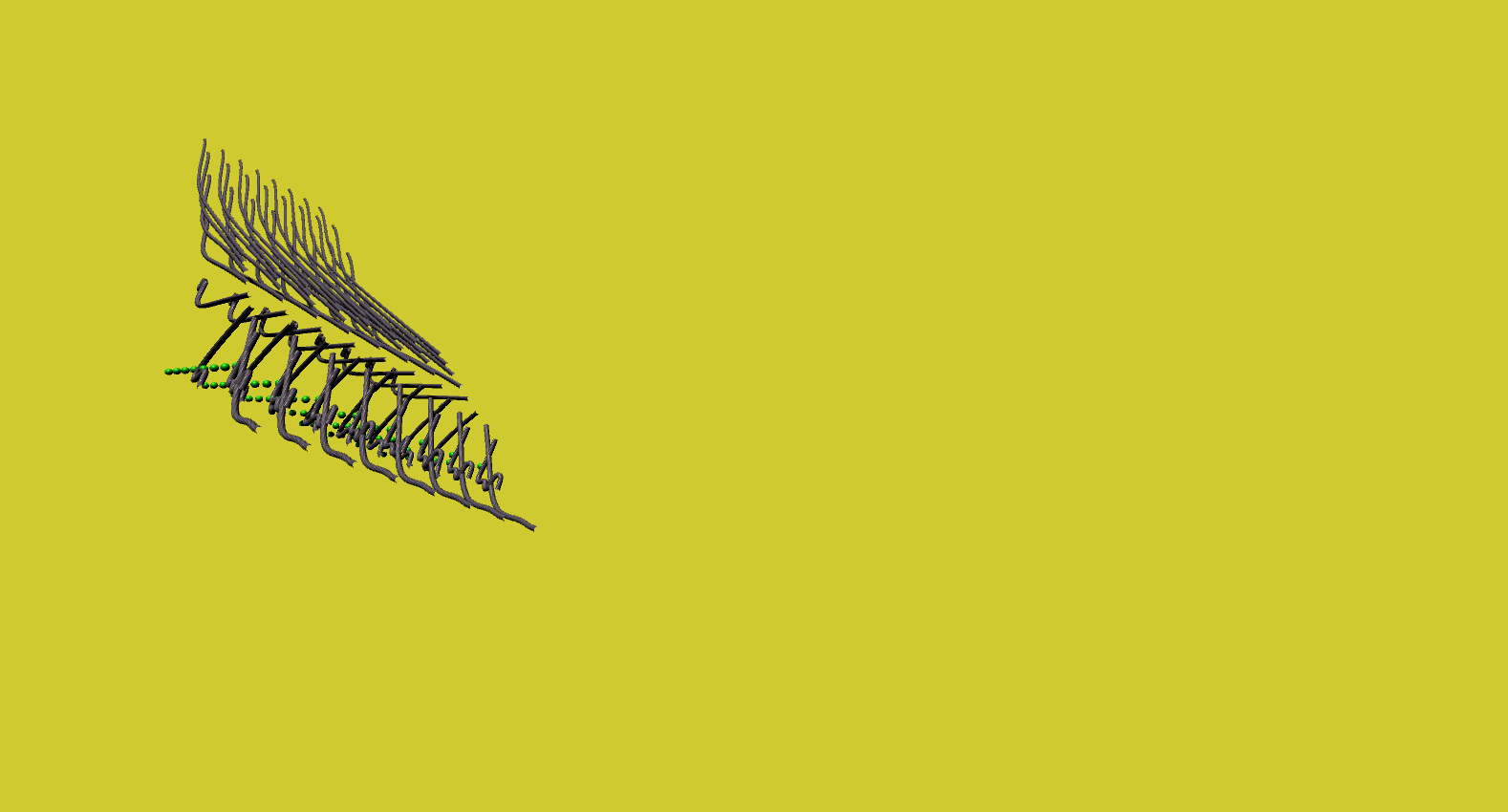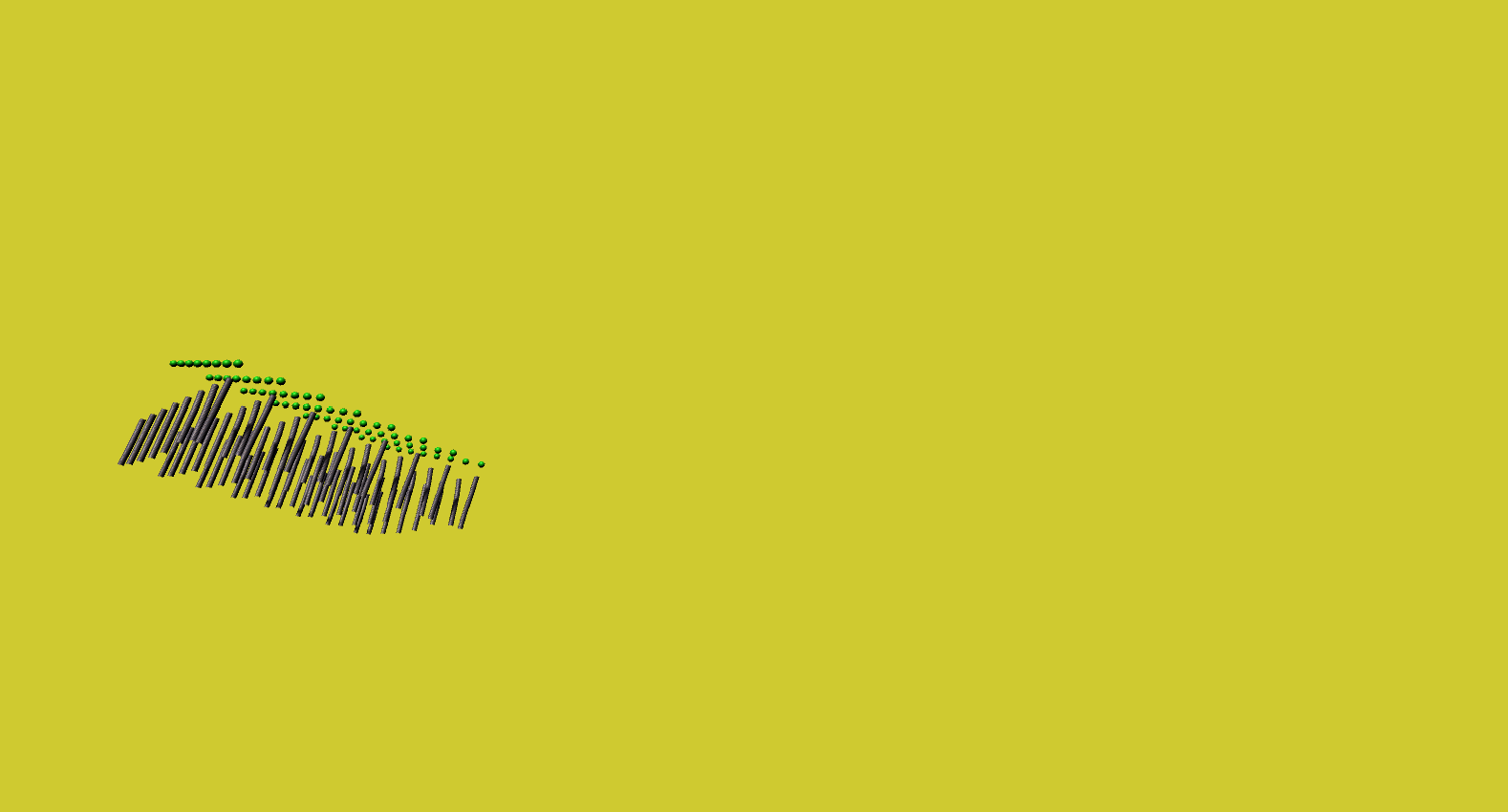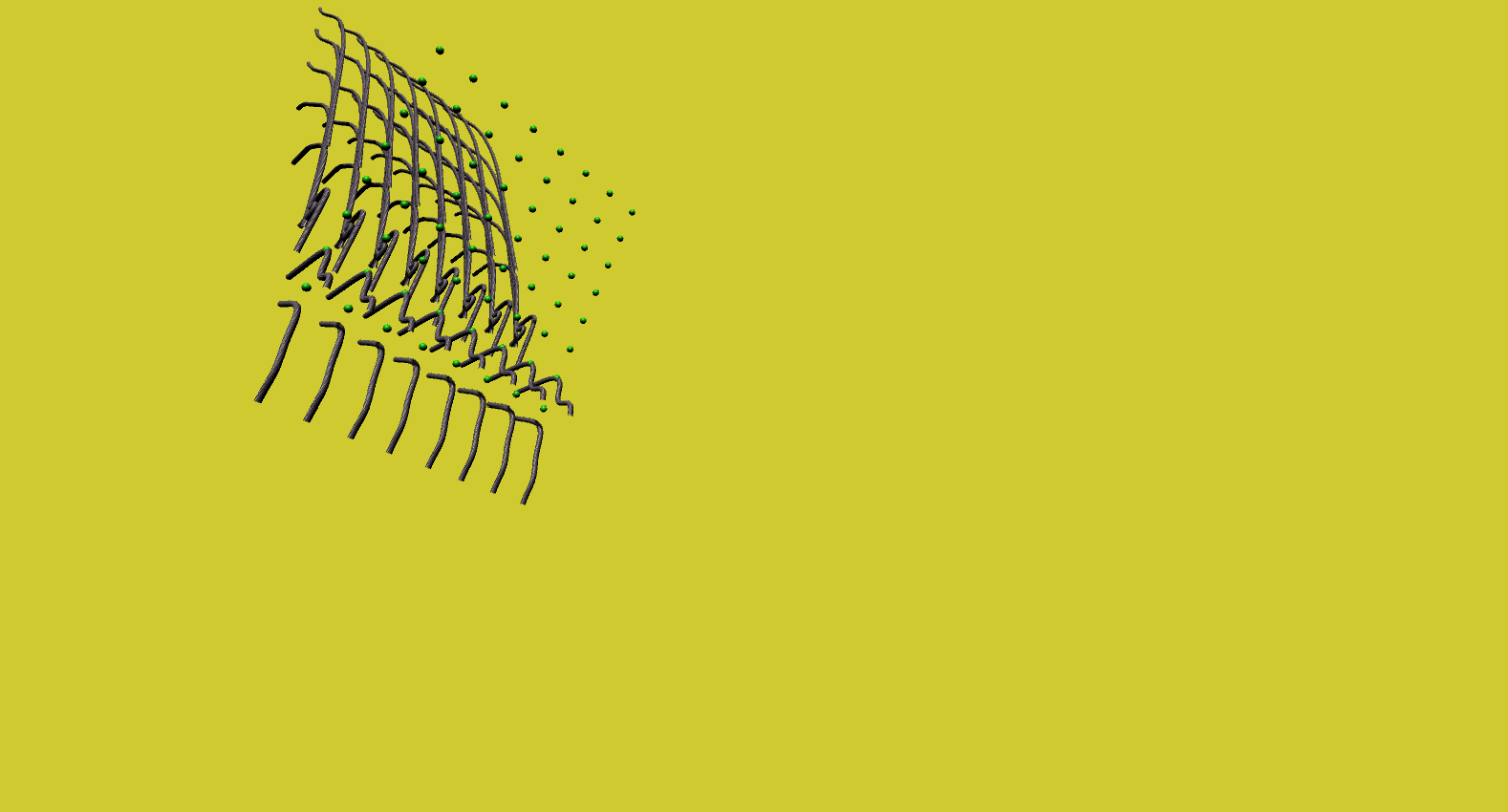
Butterfly in the Matrix
Here, a series of matrix transformations - scale, rotation, reflect and shear - were applied to a matrix of game objects, then recorded using a procedurally animated camera object to convey the concept of a butterfly lost on the matrix.